young's modulus polymer compression testing|Compression Properties ASTM D695 : Brand manufacturer Measuring and calculating Young's Modulus is crucial to understanding the mechanical behavior of polymers. This value provides valuable insight into how a polymer will respond to applied stress and strain, making it essential in .
22 de jan. de 2024 · Estratégias básicas para jogar Spaceman. Ao aprender as estratégias básicas do jogo Spaceman, lembre-se de que, como qualquer outro jogo de azar, ele .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Descargar Dark Sector PC Mega, Mediafire. Juego Dark Sect.
ASTM D695 measures the compressive strength, compressive yield point, and modulus of a material. These properties describe how the material behaves under compression, which is important information for engineers and designers working with plastic components.
This describes compressive property tests for plastics and gives average values of compressive strength and compressive modulus for common polymers such as nylon, polycarbonate, polystyrene, and polyimide.
Young's Modulus of Polymers
What is Compression Testing? The Theory and
Abstract. Analytical solutions are derived for the compression of cylinders with bonded surfaces and with Coulomb friction conditions at the interfaces. The bonded solution .Modulus of Elasticity (Young’s Modulus): The modulus of elasticity is a measure of a material’s stiffness or its resistance to elastic deformation under load. In a compression test, the modulus of elasticity can be calculated from . Compression testing is used to determine how a product or material reacts when it is compressed, squashed, crushed or flattened by measuring fundamental parameters that determine the specimen behavior .Measuring and calculating Young's Modulus is crucial to understanding the mechanical behavior of polymers. This value provides valuable insight into how a polymer will respond to applied stress and strain, making it essential in .
We precisely determine the compression modulus, plateau onset, and onset of densification strain for EPP foams across various densities.Young’s modulus is defined as the ratio of stress to strain within the elastic limit of a material. This modulus helps engineers predict how materials will respond to external forces and determine their suitability for specific applications. .Results from tensile testing include the yield point, tensile (Young’s) modulus, tensile strength, elongation, break point, and toughness. Flexural testing is performed in accordance with . Compression testing and flexural modulus evaluation are pivotal in quality control and material selection processes. Manufacturers rely on these tests to ensure materials meet specified behavioral requirements and to .
Tensile or Compressive Stress, Strain, and Young’s Modulus. Tension or compression occurs when two antiparallel forces of equal magnitude act on an object along only one of its dimensions, in such a way that the object does not . where σ is the compression stress, G is the elastic modulus, and α is the ratio of the thickness of the gel before and after compression. The plot of σ vs. ( α − α −2 ) showed a linear .Attribute Tensile Modulus Young's Modulus; Definition: Tensile modulus measures a material's resistance to deformation under tensile stress. Young's modulus measures a material's stiffness or elasticity.
The compression modulus or elastic modulus (E C) is the main parameter characterizing the linear-elastic regime (region I in Figure 1) and is defined as the slope of the linear region in the stress–strain curve.The compression modulus is widely used in the literature to compare the linear elastic behavior of bead foams. 2, 3, 6-12 However, an accurate .Compression testing was conducted for polymers, composites, and elastomers and can also be conducted on plain or “open/filled hole” specimens. Remarkably, compression testing determines behavior of materials under a crushing load, and the compression and deformation at various loads is recorded to calculate compressive stress and strain.Young's Modulus. Young's modulus is the ratio of stress to strain. It also is called the modulus of elasticity or the tensile modulus. Young's modulus is the slope of a stress-strain curve. Stress-strain curves often are not straight-line plots, indicating that the modulus is changing with the amount of strain.
A macroscopic compression test utilizing a simple custom-built instrument was employed to measure polydimethylsilox- ane (PDMS) elastic modulus. PDMS samples with varying crosslinking density were prepared with the elastomer base to the curing agent ratio ranging from 5 : 1 to 33 : 1. The PDMS network elastic modulus varied linearly with the amount of .where E c (MPa) represents the Young’s modulus of compression of the PETG plastic material. Table 7, Table 8 and Table 9 show the magnitude of the Young’s modulus obtained for each direction of analysis (X, Y and Z, respectively). These values were determined as the arithmetic mean of the elastic modulus obtained from the test specimens. A simple method for measuring the Young's modulus of thermoplastic polymers at the nanoscale is proposed. Nanoindentation tests have been carried out on three polymers (ABS, PET and PP) using the Berkovich indenter tip. The elasticity moduli obtained from the reduced moduli thanks to the slope of the initial part of the discharge curve were greater than . In this paper, polymeric specimens are produced via the Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) technique. Then, experimental tensile and compression tests are conducted to evaluate the main mechanical properties of elements made of PolyLacticAcid (PLA) material. A standardized characterization test method for FDM 3D printed polymers has not been .
Using the simple compression test to determine Young’s
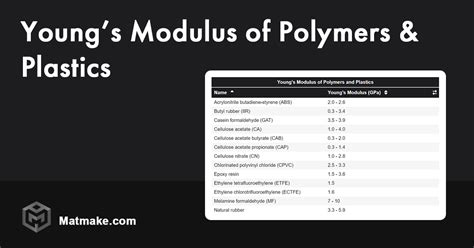
Table A3. Young’s modulus and yield strength Polymers Young’s modulus (GPa) Yield strength (MPa) Elastomers Butyl rubber (IIR) 0.001 – 0.002 2 - 3 Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) 0.01 – 0.04 12 - 18 Natural rubber 0.0015 – 0.0025 20 - 30 Polychloroprene (Neoprene) 0.0007 – 0.002 3.4 - 24 Polyisoprene rubber 0.0014 – 0.004 20 - 25Young's modulus assess how a polymer responds to external forces. See typical stiffness values for various plastics to guide your material selection. . Apart from Young's modulus, the tensile test results can also calculate: Tensile strength (at yield and at . These fundamental parameters include the elastic limit, which for "Hookean" materials is approximately equal to the proportional limit, and also known as yield point or yield strength, Young's Modulus (these, although mostly associated with tensile testing, may have compressive analogs) and compressive strength.As reported earlier, compression testing can reveal the ultimate compressive strength, yield strength, elastic modulus, and toughness of a sample. Tensile testing is done in a similar manner but rather than being compressed between two platens the sample is connected on either end to tensile testing grips.
Young's modulus value varies greatly with the material. Some Young's modulus values are given below for different random materials. Rubber young’s modulus is approximately equal to 0.01-0.1 GPa. The low-density . Quick Summary Young’s modulus is an important material property in engineering: It is a measure of the stiffness of a material (i.e. a measure of how much a material will deform when acted on by a force). .
The clasping is peculiar to the compression test and is highly influenced by the material’s elastic modulus and the sample’s strain. . and is determined through experimental testing. Compressive strength is essential .
The average in-plane compression modulus data of one half of the structurally stitched [A1-(B/2) S-A2] 2-HTA laminates (K 2, K 3, K 4, K 7, K 11, K 12 and K 14) lie within the scatter band of the corresponding unstitched laminate (Fig. 14.8).Together with the remaining data which exceed the upper margins of the scatter band, a clear tendency, especially with respect to the effect of the . Adjust the testing machine's crosshead until it slightly touches the top of the compression tool plunger. Note: Compression tool might not be essential for testing lower modulus material (e.g., 700 MPa to 3500 MPa or 100,000 psi to 500,000 psi) if loading surfaces remain smooth, flat, and parallel. Thin Specimen Placement in Jig:The compression testing was not performed on the full recommendation of ASTM D6641 . 2.2.3. Tensile–Tensile Cyclic Test . The Young’s modulus of plain fabric GFRP-RT500 was 1.82 times higher in comparison with fiber reinforced composites (GFRP-MAT450). . ASTM D6641-09 Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Polymer Matrix . They allow important information such as a material's elastic modulus and yield stress to be determined. Accurate knowledge of these parameters is paramount in engineering design. Polymer stress-strain curves are produced by stretching a sample at a constant rate through the application of a tensile force.

Young's modulus (E or Y) is a measure of a solid's stiffness or resistance to elastic deformation under load. It relates stress (force per unit area) to strain (proportional deformation) along an axis or line.The basic principle is that a material undergoes elastic deformation when it is compressed or extended, returning to its original shape when the load .Young's Modulus is reported commonly as N/mm2 (lbs/in2), MPA (psi). Typical graph showing modulus of elasticity / Young’s Modulus: We provide force measurement instruments and materials testing machines for elasticity testing. Request more information to see how we can help you with an elasticity testing solution that suits your needs.Fig. 8.8 shows a polymer test coupon in compression test. Figure 8.8. . The failure strain will decrease and for materials with different tensile and compressive elastic modulus, the stiffness of the composite will probably be affected by the thermal stresses.
The most common approach involves subjecting a material to tensile or compressive forces and measuring the resulting strain. By dividing the stress (force per unit area) by the strain (deformation per unit length), Young’s modulus can be determined. . The Young’s modulus of polymers depends on factors such as molecular structure, cross .
Understanding Young's Modulus: Key to Material
During this stage, the Young’s modulus of elasticity can be measured (which is the slope of this linear region of a stress-strain curve). Further compression will reveal the elastic limit (approximately equal to the proportional limit) and also known as yield point or yield strength. . Properties that can be measured with a compression test . This study was initiated based on the observation that standardized test methods for flatwise compression of foam materials, give significantly different test results for the measured moduli, and that these standards to date lack adequate instructions on how the strain should be measured and what specimen size should be used.

Understanding Compression Testing and Flexural
Mechanical Testing of Plastic, Rubber, Elastomer, and
Compressive Strength Testing of Plastics
webRita Cadillac fodendo com Pitt Garcia em uma ilha deserta. fotos: Rita Cadillac fodendo .
young's modulus polymer compression testing|Compression Properties ASTM D695